MagAO
MagAO is an adaptive optics instrument of the 6.5 m Magellan Clay telescope at at Las Campanas Observatory, Chile. The adaptive optics system consists of the 585 actuator adaptive secondary mirror of the Magellan telescope and a modulating Pyramid wavefront sensor. The goal of MagAO is to provide high spatial resolution imagery. The AO system feeds two different science cameras – VisAO is a visible light camera (600-1050 nanometer) and Clio2 a near-infrared camera (1 – 5.3 micrometer). At the moment of installing MagAO in 2013 it produced the sharpest visible-light images to date as it has a resolution limit of 20 milliarcseconds.

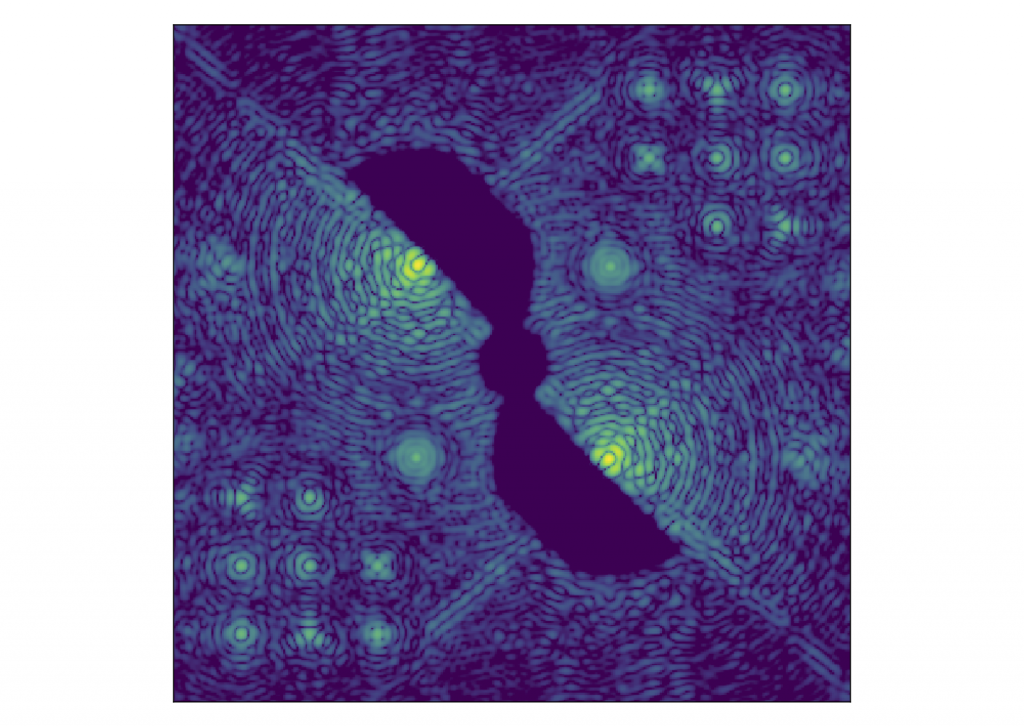
MagAP/Clio2 hosts the first vAPP that has been tested on-sky. This vAPP has been designed to provide one-sided dark holes from 2 to 5 micrometer. During the on-sky commissioning run it was found, for a bright star (L-band magnitude of 0 – 1,) that at 3.9 micrometer the vAPP delivers a 5 sigma contrast of 10^-3.3 at 2.5 lambda/D and 10^-4.8 at 3.5 lambda/D.

MagAO-X
MagAO-X is the new high-contrast imaging instrument located at the Nasmyth platform of the Magellan Clay telescope. The main science goal is to directly image newly forming exoplanets in H-alpha. The AO system in MagAO-X itself consists of a woofer-tweeter system. That means the first deformable mirror (DM), an Alpao DM with 97 actuators, provides an initial low-order correction to the beam, and that the second DM, a Boston Machine DM with 2000 actuators, provides the high-order wavefront correction. The main wavefront sensor is a modulated Pyramid wavefront sensor, similar to what is installed for MagAO.
The current coronagraph installed is the vAPP designed to provide a contrast of 10^-5 between 2 and 15 lambda/D from 550 to 900 nm. Besides that this vAPP provides a dark hole, this also contains three different focal-plane wavefront sensors. A pair of holograms biased with strong diversity for phase diversity, twelve additional pairs of holograms biased with low-order Zernike aberrations for the coronagraphic modal wavefront sensor, and a pupil amplitude asymmetry integrated in the vAPP design enables spatial LDFC.